Email is one of the most powerful tools for businesses today. It helps you reach customers, share updates, and build relationships. But if your emails don’t reach inboxes or are marked as spam, your message won’t be seen.
One of the main reasons this happens is poor email authentication. Without the right settings, email providers can’t verify that your emails are coming from you. As a result, your emails are blocked or sent to the spam folder.
That’s why it’s important to set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records correctly. These tools help improve your email’s deliverability. They tell email providers that your messages are genuine and safe.
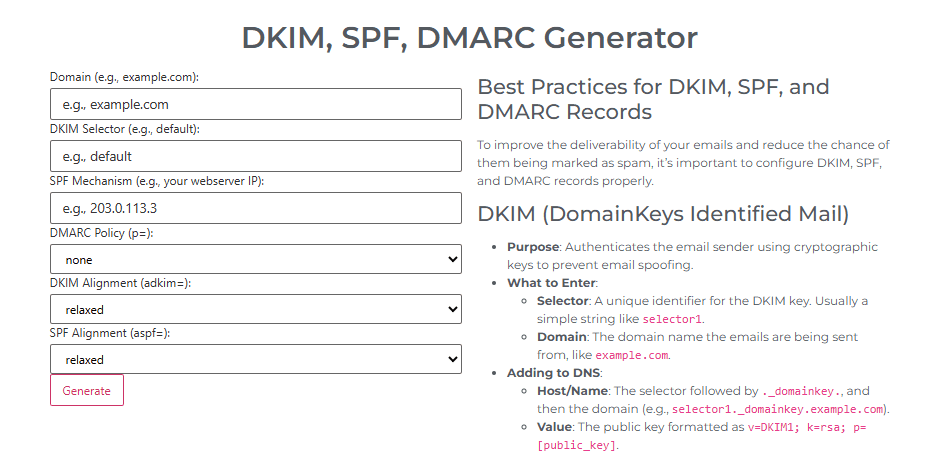
Setting up these records sounds technical, but it doesn’t have to be hard. McElligott Digital Marketing’s DMARC, SPF, and DKIM generator can help you create the right records easily. With the correct setup, your emails are more likely to reach your audience and avoid spam filters.
In this blog, we’ll explain what SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are and how they work. By the end, you’ll understand how to configure them properly to improve your email deliverability.
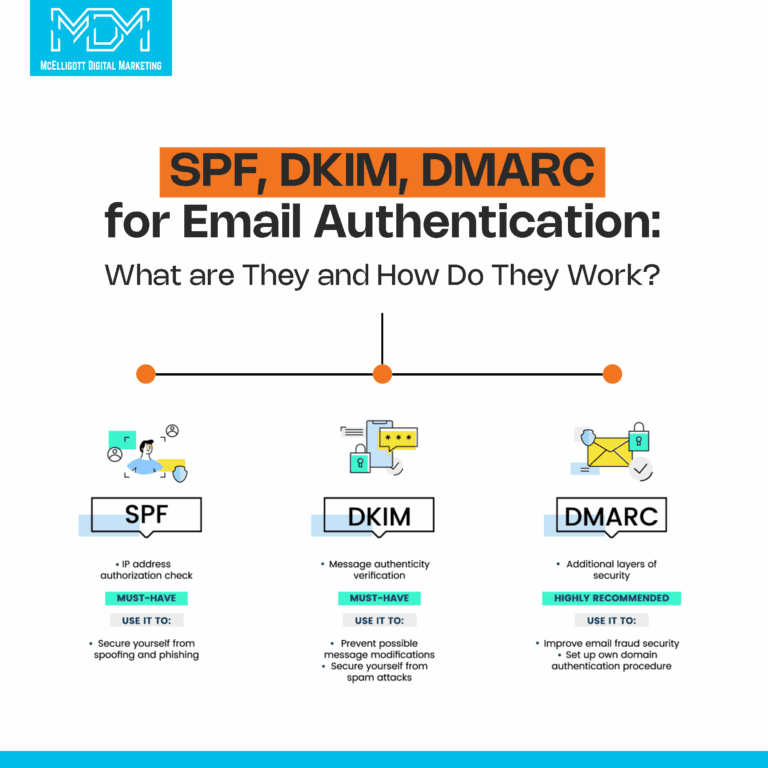
What is SPF in email authentication?
SPF stands for Sender Policy Framework. It is one of the first steps in email authentication. It helps email servers check if your email is sent from an approved source.
When you send an email, your domain name is used in the “From” address. But spammers can fake this and send emails that look like they are coming from you. SPF helps prevent this by telling email providers which servers are allowed to send emails on your behalf.
You set up SPF by creating a record in your domain’s DNS settings. This record lists all the servers or IP addresses that are allowed to send emails using your domain name.
When someone receives your email, their email provider checks your SPF record. If the email comes from a listed server, it passes the check. If not, the email is marked as spam or rejected.
Why is SPF important?
It improves the chances that your emails will reach your customers. It also protects your brand from being used in spam or phishing attacks.
However, SPF has some limitations. For example, if your email is forwarded, the forwarding server might not be listed in your SPF record. This can cause your email to fail the check.
Despite this, SPF is a useful tool that works with DKIM and DMARC to strengthen your email security and deliverability.
What is DKIM in email authentication?
DKIM means DomainKeys Identified Mail. It adds a digital signature to your emails. This proves that the email really came from you and hasn’t been changed on the way.
When you send an email, DKIM attaches a special signature to it. This signature is created using a private key. The email provider receiving your message uses a public key to check this signature.
The public key is stored in your domain’s DNS settings. When the receiving server gets your email, it looks up this key and verifies the signature. If the signature is correct, the email is accepted as safe. If it’s not, the email may be marked as suspicious or spam.
Why do you need DKIM?
It protects your emails from being altered by hackers. It also shows that your message is authentic. This builds trust with email providers and improves your chances of reaching customers.
Unlike SPF, DKIM still works even if your email is forwarded. That’s because the signature stays with the message. However, it’s important to set it up correctly and ensure your DNS records are accurate.
Using DKIM along with SPF gives you better protection. It helps ensure your emails are verified and improves deliverability.
What is DMARC?
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance, or DMARC, builds on SPF and DKIM to give you more control over your emails.
With DMARC, you can tell email providers how to handle messages that fail authentication checks. It lets you set rules to protect your domain from fake emails.
You create a DMARC record in your domain’s DNS settings. In this record, you choose a policy for how emails should be treated. There are three main options:
- None– Just monitor emails. No action is taken if they fail.
- Quarantine– Emails that fail checks are sent to the spam or junk folder.
- Reject– Emails that fail are blocked and not delivered.
DMARC also lets you receive reports. These reports show you which emails are passing or failing the checks. You can use this information to improve your settings and keep your domain safe.
Need for DMARC
It helps protect your brand’s reputation. It also improves your email deliverability by reducing the chances that your emails are seen as spam.
Together with SPF and DKIM, DMARC creates a strong defense. It ensures your emails are trusted and more likely to reach your customers.
How SPF, DKIM, and DMARC work together?
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are three tools that help your emails get delivered safely. Each one has a different job, but together they create a strong email authentication system.
Here’s how they work.
1. SPF checks where the email is coming from.
It looks at the sender’s IP address and compares it with the list of allowed servers in your DNS settings. If it matches, the email passes this check.
2. DKIM checks if the email has been tampered with.
It uses a digital signature attached to the email. The receiving server verifies this signature using the public key stored in your DNS.
3. DMARC combines both checks and adds a policy.
It tells the receiving server what to do if the email fails SPF or DKIM checks. It can allow, check, or reject the message based on your settings.
When an email is received, the server first looks at the SPF record. Then it checks the DKIM signature. After that, it follows the DMARC policy you’ve set up. Using all three makes it harder for spammers to misuse your domain.
Setting up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC together is the best way to improve email deliverability. It helps you build trust with email providers while protecting your brand.
How to implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC?
Setting up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC sounds technical, but it’s something you can do with a few simple steps. Once configured correctly, these tools will help your emails reach inboxes and avoid being marked as spam.
Step 1- Set up SPF
- Go to your domain’s DNS settings.
- Create a new TXT record for SPF.
- List the servers or IP addresses allowed to send emails from your domain.
- Example format-
v=spf1 ip4:192.168.0.1 include:example.com -all
- Save the record and test it using tools to make sure it’s working.
Step 2- Set up DKIM
- Generate a DKIM key pair (private and public keys).
- The private key is used by your email server to sign outgoing emails.
- The public key is added as a TXT record in your DNS.
- Give your DKIM record a selector name like default._domainkey.
- Once set, test the signature to ensure it’s valid.
Step 3- Set up DMARC
- Create a DMARC record as a TXT entry in your DNS.
- Specify your preferred policy- none, quarantine, or reject.
- Include your email address to receive reports.
- Example format-
v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; rua=mailto:reports@example.com;
- Save and monitor reports to adjust settings if needed.
Conclusion
Setting up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC is essential for improving your email deliverability. These tools help email providers trust your messages and reduce the chance of them being marked as spam. With the right setup, you can protect your brand and ensure your emails reach the right audience.
Need help configuring these records or want expert advice on improving your email deliverability?
Reach out to us for a FREE consultation at (833) 772-489.
We’ll guide you through the process and ensure your emails get the attention they deserve.